
Financial services giant JPMorgan has unveiled a "lightweight" AI model extension called DocLLM that aims to advance comprehension of complex business documents like forms, invoices, and reports. DocLLM is a transformer-based model that incorporates both the text and spatial layout of documents to better capture the rich semantics within enterprise records.
The key innovation in DocLLM is the integration of layout information through the bounding boxes of text extracted via OCR, rather than relying solely on language or integrating a costly image encoder. It treats the spatial data about text segments as a separate modality and computes inter-dependencies between the text and layout in a "disentangled" manner.
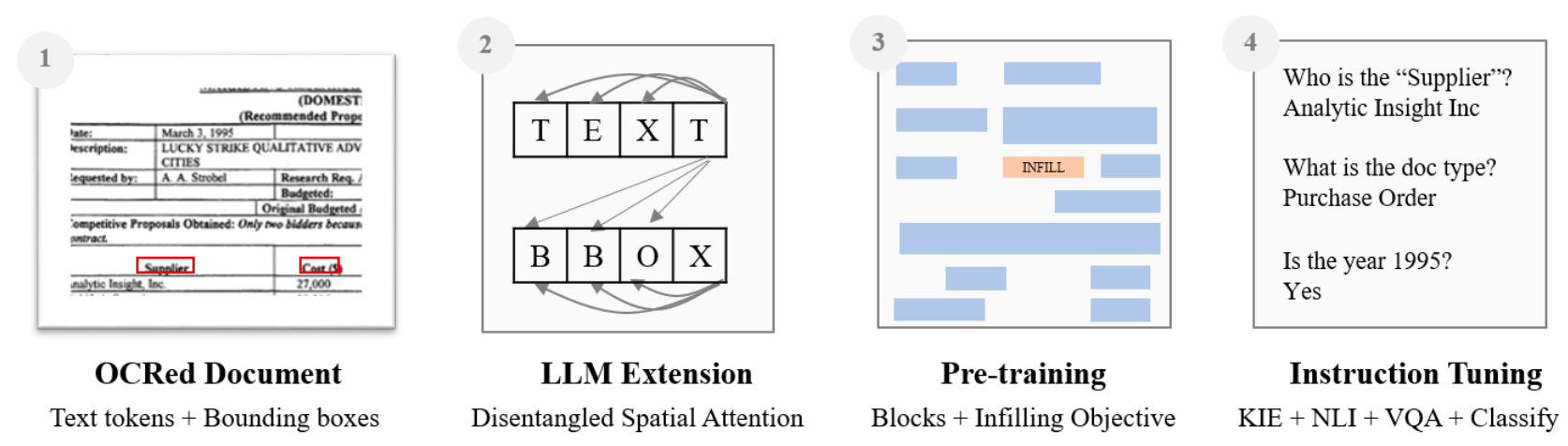
Specifically, DocLLM extends the self-attention mechanism in standard transformers with additional cross-attention scores focused on spatial relationships. This allows the model to represent alignments between the content, position, and size of document fields at various levels of abstraction.
To handle the heterogeneous nature of business documents, DocLLM also employs a text infilling pre-training objective rather than simple next token prediction. This approach better conditions the model to deal with disjointed text segments and irregular arrangements frequently seen in practice.
The pre-trained DocLLM model is then fine-tuned using instruction data curated from 16 datasets covering tasks like information extraction, question answering, classification and more.
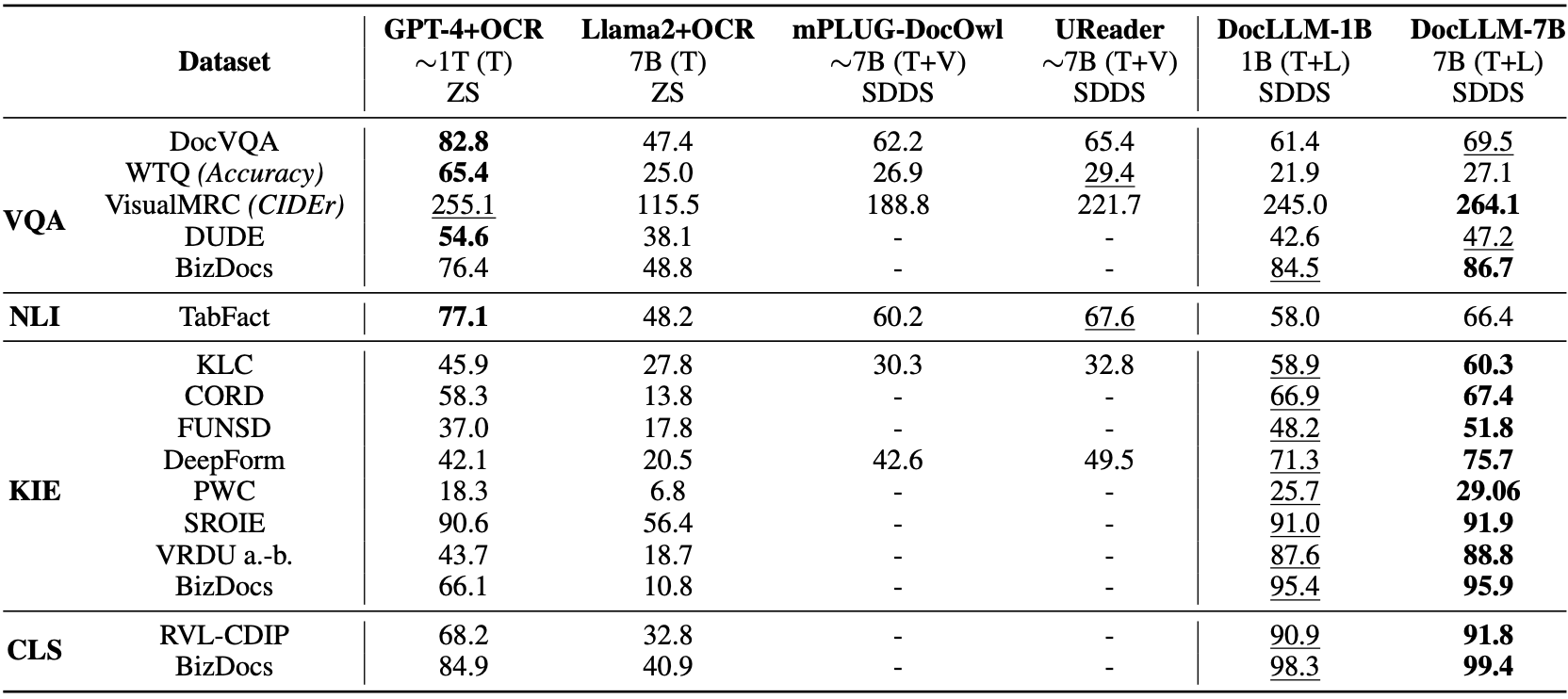
In evaluations, DocLLM achieved state-of-the-art results on 14 of 16 test datasets on known tasks, demonstrating over 15% improvement on certain form understanding challenges compared to leading models like GPT-4. It also generalized well to 4 out of 5 unseen test datasets, exhibiting reliable performance on new document types.
The practical implications of DocLLM are substantial. For businesses and enterprises, it offers a promising new technique for unlocking insights from the huge array of forms and records used daily. The model may enable more automated document processing and analysis for financial institutions and other document-intensive businesses going forward. Furthermore, its ability to understand context and generalize to new domains makes it an invaluable tool for various industries, especially those dealing with large volumes of diverse documents.

