OpenAI has unveiled Reinforcement Fine-Tuning (RFT), a model customization technique that will allow businesses to build highly specialized AI models for complex, domain-specific tasks. By using RFT, users can train models to reason like experts in fields like law, medicine, finance, and engineering—leveraging the same technology OpenAI uses to develop its own frontier models.
Key Points:
- Reinforcement Fine-Tuning allows organizations to train expert AI models with as few as a dozen examples, using reinforcement learning to refine reasoning.
- OpenAI’s alpha program is available now, with a public release planned for early 2025.
- RFT has demonstrated success in fields like law, healthcare, and engineering, enabling advanced, task-specific capabilities.
- The technique differs from supervised fine-tuning by teaching models how to reason and solve problems, rather than simply mimicking input data.
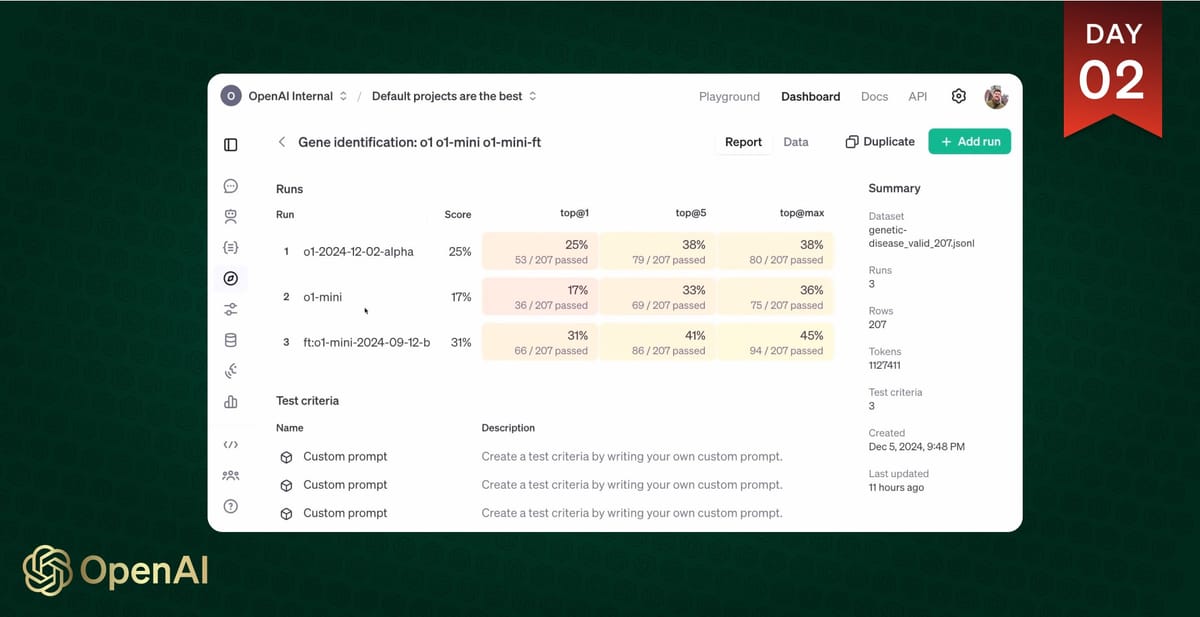
In the livestream, Justin Reese, a computational biologist from Berkeley Lab showed how RFT improved the model's ability to identify genetic causes of rare diseases. "Assessing rare disease is kind of hard because you have to have two things: expert domain knowledge about the medical side of things and systematic reasoning over the biomedical data," Reese noted during the presentation.
Why it matters: RFT is a big step forward in AI customization, allowing enterprises to train models for precise, domain-specific tasks. Unlike traditional fine-tuning, RFT improves a model’s ability to reason through problems rather than just replicate patterns. This advancement could redefine how businesses use AI in fields requiring deep expertise.
How it works: RFT leverages reinforcement learning to guide models toward better reasoning. Users provide datasets and grading criteria, called graders, to score model outputs. These scores guide the training process, refining the model’s reasoning capabilities to handle complex, high-stakes tasks effectively.
The technology's effectiveness was particularly evident in the demo, where a fine-tuned version of GPT-4 mini outperformed the base GPT-4 model on specific tasks. The fine-tuned model achieved a 31% accuracy rate in identifying correct genes on the first try, compared to 25% for the base model.
Who benefits: RFT is ideal for industries where accuracy is critical, such as legal analysis, scientific research, and financial forecasting. OpenAI has already partnered with organizations like Thomson Reuters to develop legal AI tools, demonstrating the potential for transforming workflows in expert-driven domains.
Looking ahead: OpenAI has launched an alpha program for RFT, encouraging enterprises, universities, and research institutes to apply. Participants will gain early access to the RFT API and provide feedback to refine the tool ahead of its full release in early 2025.
Reinforcement Fine-Tuning has the potential to democratize access to cutting-edge AI, enabling organizations to build tailored solutions that meet their unique challenges. With its ability to adapt models using minimal data, RFT could become a cornerstone for innovation across industries.

